Fastag: Everything you need to know
The missing piece in the logistics puzzle.
Have you felt so much time wasted in toll booths?
Have you lost your patience in these situations?
Do you know the reason for your precious time getting wasted in these circumstances?
By this time you could have found out what this article is going to be about. Yes, it is definitely about Toll systems and Indian FASTag.
You will get to know a lot about toll systems,in simple words its their comparison with FASTag . Also, you will get a brief knowledge of what is FASTag, its features, and usage in real-time technologies. So better give a read to understand various toll systems and FASTag in depth.

We all know that manual toll collection is the collection of money by a toll collector or an attendant in toll booths. But do we all know why we pay taxes in toll booths? If you know please ignore my answer. We pay in toll booths outside cities to use certain roads crossing which we can reach our destination. As of now manual toll booths are of great use and is also beneficial for all class of drivers. But the only disadvantage is that for persons traveling along the route they have to stand in many toll booths to travel through that route. This will owe them wastage of their precious time which in turn will make them reach their destination late. This will put that driver or that person into trouble if they have to reach a destination in case of any emergency.
To overcome the problems faced in manual toll collection, Electronic Toll Collection (ETC) comes into the picture. Like manual toll collection, ETC also allows the collection of several methods of payments such as coins, tokens, smart cards, and credit cards. ETC is a complex and latest technique used in toll booths in many parts of the world and continues to evolve day by day. By bringing ETC to use, speed and efficiency of the traffic flow can be improved which in turn saves driver’s time and effort.
ETC functions mainly in the following manner. When the vehicle passes a roadside toll reader device, a radio signal from the reader triggers the transponder, which transmits back an identification number that registers the vehicle’s use of the road, and an electronic payment system charges the user for the toll usage. Some facts also say that electronic tolling is cheaper than manual tolling because electronic tolling reduces transaction costs for government or private road owners. This system usually asks users to sign up their portal, open a new account in their mentioned bank, and whenever that vehicle passes through the toll booth, their account will be debited with respective toll charges. Electronic toll booths should be placed alongside conventional toll booths so that for vehicles whose transponders don’t respond at that time can pay manually using manual toll collection booths.
Some electronic toll collection systems used across the world
Salik toll collection system in Dubai
Salik is the name of the electronic toll road system in Dubai, United Arab Emirates which was launched by Dubai Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) on 1st July 2007. This system is entirely based on RFID technology which automatically deducts a fee when vehicle is passes under toll gates. The main advantage of this system is that there are no toll booths, barriers, or physical gates, so you can drive straight through the toll gates at normal highway speed. Each time when a vehicle passes through a toll point, a toll of a particular amount is deducted from the user’s prepaid toll account using advanced Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. When the Salik tag was first introduced the vehicle was charged continuously six times and after six times it was free but now that rule has been removed by RTA. Salik is mainly the name of the tag or sticker placed on the vehicle which operates without battery and moving parts and works in all weather conditions and speeds. It also provides accurate identification for the vehicle to the system.
Salik toll collection system in Dubai
Salik is the name of the electronic toll road system in Dubai, United Arab Emirates which was launched by Dubai Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) on 1st July 2007. This system is entirely based on RFID technology which automatically deducts a fee when vehicle is passes under toll gates. The main advantage of this system is that there are no toll booths, barriers, or physical gates, so you can drive straight through the toll gates at normal highway speed. Each time when a vehicle passes through a toll point, a toll of a particular amount is deducted from the user’s prepaid toll account using advanced Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. When the Salik tag was first introduced the vehicle was charged continuously six times and after six times it was free but now that rule has been removed by RTA. Salik is mainly the name of the tag or sticker placed on the vehicle which operates without battery and moving parts and works in all weather conditions and speeds. It also provides accurate identification for the vehicle to the system.
Electronic toll collection (ETC) in Japan
This system is also an ETC system but the difference between ETC and the Salik collection system is that the former is based on wireless communication that exists between the antenna installed at the tollgate and the ETC onboard device in the vehicle. To use the ETC system, you must have a vehicle onboard device, and an ETC card issued by your credit card company must be inserted into the device. All the payment details of the user are stored in the ETC card placed inside the onboard device. The main advantage of this system is that unlike other systems not only owners anyone can drive the vehicle if they have the ETC card issued with them. On reading the previous line I know you all will get a feeling about whether ETC in Japan is secure or not. It’s a secure system with a series of advanced security procedures such as mutual authentication between the ETC card and the onboard unit, encryption of data, and tampering check prevents recorded data from spoofing, tampering, and forgery, etc.
e-TAG toll collection system in Australia
e-TAG is a free-flow toll collection system (cashless toll collection system) used by people throughout Australia. This system was originally developed by Transurban, a road operator company in Australia which was used by all toll roads, bridges, and tunnels in Australia. e-TAG was one of the first surcharge-free toll collection systems in providing tolling services across many states amongst rival tolling service providers. Like the Salik toll collection system, this system also uses RFID technology and DSRC protocol for processing toll gate charges. Gantries that are constructed over carriageways record registration plates and detect e-TAGs and the software associated takes care of the toll amount payable by the customer which is debited from his pre-paid account associated with the tag. When a tag is not detected, the vehicle’s registration is recorded using video tolling technology which incorporates an automatic number plate recognition system and checked against a government motor registration database. If payment has not been made after three days, the vehicle’s registered owner will be sent a late toll invoice in the mail, and if the late toll invoice is then not paid a fine will be issued.
Electronic toll collection (ETC) system in Taiwan
This system was used to collect tolls electronically on national highways in Taiwan. Taiwan was the first country to switch from a manual tolling system to an Electronic Tolling System. Here surcharges were collected mainly considering the distance traveled by the vehicle, speed, and the load amount . For example, buses and trailers were surcharged with heavy fees compared to other vehicles. The highway administration may alter fares during peak travel seasons to facilitate the distribution of congestion to midnight hours. Each vehicle receives a further discount after the first 200 kilometers, and eTag subscribers with prepaid accounts get a further 10% reduction. Non-subscribers are billed by license plate recognition and mail statements or can make a payment at a chain convenience store on the third day after vehicle travel since a subscription to ETC is not mandated by law. ETC tag in Taiwan can produce 99.999% accurate results.
FASTag, an Indian electronic toll collection system
Till now Indians would have felt that all countries have implemented Electronic Toll Collection systems why not we? So also to make Indians access electronic toll system,the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI), an autonomous national agency responsible for the management of large areas of National Highways have introduced FASTag, anETC system in India which operates perfectly satisfying all the needs and requirements of the customers using it. Like all efficient ETC systems used across the world, FASTag also uses RFID technology to make toll payments from the vehicle owner’s prepaid or savings account to toll owners’ account. FASTag is going to be made as a compulsory toll collection in India from January 2021.
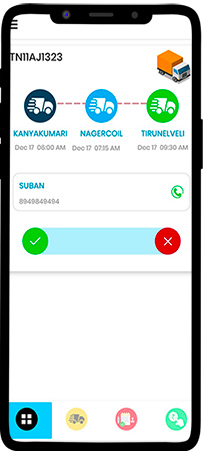
Step 1: The driver accepts a trip that was created in the FleetOS app by the fleet manager.
The words given on this screen can be in any language as per the Fleet Manager’s preference.
The contact number given is the contact details at the first point where the driver should reach.
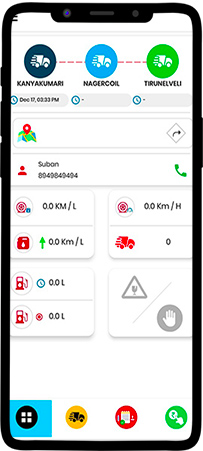
On accepting the trip, the driver can see the following details in the DashBoard. Vehicle Pick up location, Loading location, and unloading location — along with planned date and time.
The application opens a new screen by clicking the Map symbol, which directs the driver to the first destination point.
Other details on this screen are
Milage — Expected & Actuals
Speed Limit — Expected & count of Overspeed occurrences
Fuel level — Most recently filled quantity and current level.
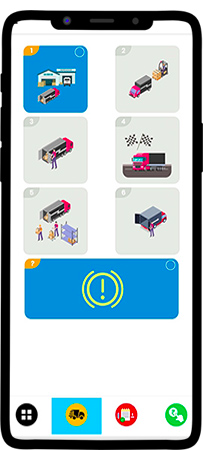
Step 2: Report Vehicle status (position) in one click.
In the loading to unloading cycle, a driver can report 6 different statuses (or positions).
1. Reached Loading point
2. Loading started
3. Loading completed
4. Reached unloading point
5. Unloading started
6. Unloading completed
7. Any other issues.
The flow is designed in such a way at any point; the driver can choose any one option.

Assume that in the above screen, the driver has chosen the first position — Reached loading point. Now the driver is prompted to add any description in voice recording or photos (both are optional) and submit the position.
Step 3: In the app, the driver can reach out to the Fleet Manager at any time by touching the third tab. Technically it’s called “Attentions raised.” Here a driver can raise 7 types of attention.
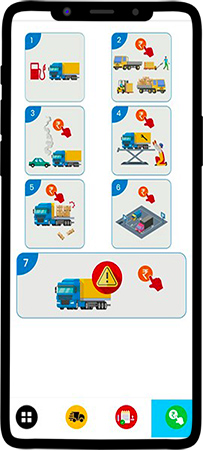
- Fuel requirement
- Loading or unloading charges
- Any accidents
- Service issues
- Goods damaged
- Parking charges
- Any other issues.
The fleet managers can respond to this “attention raised” by drivers from the FleetOS app. The driver can see the fleet manager’s response in the fourth tab. It’s technically known as the “Instructions” tab.
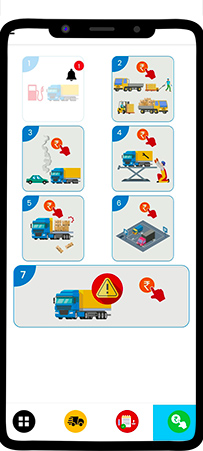
The fleet manager’s response is shown using an alarm symbol. On tapping the relevant card with an alarm symbol, a driver can see whether the fleet manager has approved or rejected, or modified the request.
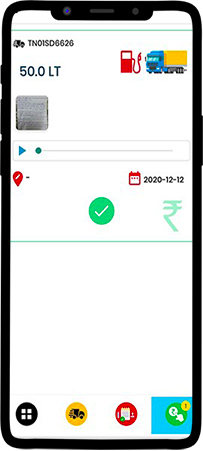
Here, in this case, the fleet owner has approved the 50-liter fuel limit request.
Key design principles we followed in designing this app.
- Minimal navigation. Maximum one step forward and one step backward.
- All tabs should be open and visible, the driver should able to navigate to any at any time.
- A fleet manager should able to address any doubts of a driver related to the app remotely. In this case, a fleet manager can just guide the driver to select an appropriate card based on the numbers. So training is very simple.
- The driver should able to upload images (docs) and voice recordings from every screen. Even if he makes mistakes, for instance, upload POD in the fuel tab, Fleet Manager should able to retag properly in his app (FleetOS).
We hope we found the missing piece in the road logistics puzzle. On efficiently engaging the driver in the digitization process, both fleet managers and drivers are tremendously benefitted.
All the complications in the lifecycle of fleet management are simplified, FleetOS app (fleet manager app) has several options to manage any mistakes made by the drivers.
To try this solution, please login into the FleetOS application + download the driver app.


